4 min read
If you’ve ever experienced tingling or numbness in your hands or wrists, you may have wondered: What’s going on here? Could it be just stress, or could it be something more? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is more common than you think, and it could be the reason behind these uncomfortable sensations. But don’t worry—this article will explain what carpal tunnel syndrome is, how it feels, how it’s treated, and how you can manage it effectively.
Whether you’re dealing with carpal tunnel syndrome right now or just curious about it, stick with us. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding and practical tips to ease your symptoms.
For personalized assistance with carpal tunnel or other neurological concerns, feel free to check out Neurology Mobile or explore the services offered at Neurology Mobile Services.
Overview of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
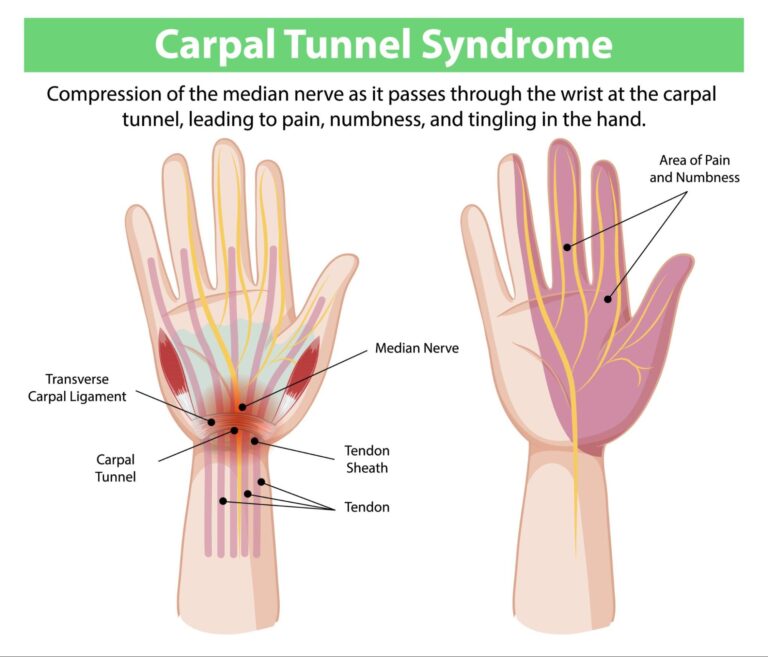
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, becomes compressed or irritated. This nerve controls the sensation in your thumb, index, middle, and part of your ring finger. When the median nerve is squeezed within a narrow passageway called the carpal tunnel, you experience symptoms like tingling, numbness, and pain in your hand and wrist.
The carpal tunnel is a small space in the wrist, surrounded by bones and ligaments, and when it becomes inflamed or compressed, it affects the nerve passing through it. The results can range from annoying to disabling, depending on the severity.
Anatomy of the Wrist and the Median Nerve
Imagine your wrist as a passageway. The median nerve runs through it, carrying vital signals to your hand. But when this passage becomes crowded—either due to injury, repetitive movements, or inflammation—the nerve gets pinched. The result? A collection of symptoms that can seriously affect daily life.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
How Does Carpal Tunnel Feel?
Have you ever felt like your hand was “falling asleep” or had a sharp, electric-shock sensation running through your fingers? That could be the early sign of carpal tunnel syndrome. Common symptoms include:
- Tingling and Numbness: This is the most common symptom. You may feel as though your fingers are “asleep,” or you might experience an electric shock sensation in your hand.
- Pain: Carpal tunnel pain can be sharp, aching, or even burning. It often happens in the wrist, hand, or fingers.
- Weakness: You might notice your grip weakening, making it harder to hold objects, whether it’s a pen or a coffee cup.
These symptoms can be more noticeable when you’re using your hands—typing, holding a phone, or even when you’re sleeping. It’s during these activities that pressure on the nerve can increase, causing more discomfort.
Tingling, Numbness, and Weakness in the Hands
Have you ever tried to shake your hand out to get rid of that annoying, numb feeling? Now imagine this sensation occurring frequently—throughout your day and even during the night. That’s the reality for many people with carpal tunnel syndrome.
If you’ve been experiencing persistent tingling or numbness that gets worse over time, it’s essential to take action. Don’t just assume it’s temporary.

Causes and Risk Factors
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The root cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. But what exactly causes that pressure? There are several factors at play:
- Repetitive Motion: Tasks that involve repetitive hand movements (such as typing or using a mouse) can gradually increase pressure on the nerve.
- Wrist Injury: Even a minor injury can alter the structure of your wrist, narrowing the carpal tunnel and compressing the nerve.
- Arthritis: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can cause swelling in the wrist, further narrowing the tunnel and putting pressure on the nerve.
Is Carpal Tunnel Genetic?
Interestingly, carpal tunnel syndrome can run in families. If your parents or siblings have had it, your risk increases. This could be due to hereditary factors that result in a smaller carpal tunnel, making it more prone to pressure on the median nerve.
Risk Factors for Developing Carpal Tunnel
Some people are at a higher risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Are you one of them? You may be more susceptible if you:
- Perform repetitive motions at work (e.g., typing, assembly line work).
- Are pregnant, as hormonal changes can lead to fluid retention that puts pressure on the wrist.
- Have certain health conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or obesity.
If any of these sound familiar, it’s a good idea to pay extra attention to your wrist health and take preventative steps.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Options
If you’re wondering what is carpal tunnel syndrome, and what can be done about it, there are several treatment options available. The good news is that many of them don’t involve surgery. Here are some common approaches:
- Wearing a Splint: A splint keeps your wrist in a neutral position and prevents it from bending during sleep or activities, easing pressure on the median nerve.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen your wrist and improve flexibility.
- Adjusting Posture: Sometimes, all it takes is adjusting the way you sit or hold your hands. Proper ergonomics can go a long way in reducing stress on your wrists.
How to Fix Carpal Tunnel: Non-Surgical Methods
In many cases, non-surgical treatments are effective in alleviating symptoms. These treatments include:
- Rest: Giving your wrists some time to recover can be one of the most helpful steps.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce inflammation and ease discomfort.
- Corticosteroids: If the pain persists, corticosteroid injections may reduce inflammation in the affected area.
But, if these treatments don’t provide enough relief, surgery might be necessary.
When Is Surgery Necessary for Carpal Tunnel?
Surgical options, like carpal tunnel release surgery, might be recommended if conservative treatments fail. The surgery involves cutting a ligament in your wrist to create more space for the nerve, thus reducing pressure. This outpatient procedure typically offers long-term relief from symptoms.
Prevention of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
How to Prevent Carpal Tunnel
If you’re wondering whether you can prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, the answer is yes—at least to some degree. Here are a few tips to keep your wrists healthy:
- Stretch and Strengthen: Regular wrist exercises can help prevent stiffness and improve flexibility.
- Take Breaks: If you work at a desk or use your hands repetitively, take frequent breaks to stretch your wrists.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Ensure your wrists are in a neutral position when typing, using a mouse, or performing any task that requires hand movement.
Tips for Reducing Risk in the Workplace
If your work involves repetitive movements, you can reduce the risk of carpal tunnel by:
- Using ergonomic tools and adjusting your workstation.
- Taking breaks to stretch your hands and wrists every hour.
- Ensuring your wrist stays in a neutral position during tasks.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Wondering what is carpal tunnel and if you might have it? The first step is to visit a healthcare professional. They’ll conduct a physical exam and may perform tests such as:
- Tinel’s Sign: A test where tapping the wrist can cause a tingling sensation if carpal tunnel syndrome is present.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity in the muscles to check if the median nerve is being compressed.
If you’re experiencing symptoms like tingling, numbness, or weakness in your wrists or hands, it’s time to get checked out. Understanding what is carpal tunnel and seeking early diagnosis can help prevent further complications.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Comparison
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
| Wrist Splints | Non-invasive, provides immediate relief during sleep. | May feel uncomfortable if worn for extended periods. |
| Physical Therapy | Strengthens muscles and improves wrist flexibility. | Takes time and consistency to see results. |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Effective for reducing inflammation. | Temporary relief; not a long-term solution. |
| Carpal Tunnel Surgery | Provides long-term relief; effective for severe cases. | Requires recovery time; carries surgical risks. |
For more help with carpal tunnel syndrome, visit Neurology Mobile or explore our services for personalized support.
Living with carpal tunnel syndrome doesn’t have to be a life sentence. By taking the right steps—whether it’s through preventive measures, non-invasive treatments, or surgery—you can manage the symptoms and protect your wrist health for the long run. Don’t wait until it gets worse—take control now and get back to doing the things you love, without the pain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is carpal tunnel syndrome, and what are the early signs of it?
The early signs of carpal tunnel syndrome typically include tingling, numbness, and a “pins and needles” feeling in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring fingers. You might notice these sensations when holding items like a steering wheel, phone, or even while sleeping. Initially, the symptoms may come and go, but if left untreated, they can become constant and lead to weakness in the hand. If you experience these symptoms frequently, it’s important to seek medical advice.
2. Can carpal tunnel syndrome go away on its own?
In some cases, mild carpal tunnel syndrome can improve on its own, especially if it’s related to temporary factors like pregnancy or fluid retention. However, if left untreated, the condition can worsen, causing permanent nerve damage. Early intervention, such as using a splint, physical therapy, or making ergonomic changes, can help relieve the symptoms and prevent further complications. If non-surgical treatments don’t provide relief, surgery might be necessary.
3. Is carpal tunnel syndrome genetic?
Yes, carpal tunnel syndrome can be hereditary. If you have a family history of the condition, you might be at a higher risk of developing it. Genetic factors could contribute to a smaller carpal tunnel, which makes the median nerve more susceptible to compression. However, other factors like repetitive motion, injury, or certain health conditions also play a role in developing the syndrome.
4. How long does recovery take after carpal tunnel surgery?
Recovery time after carpal tunnel release surgery varies depending on the individual, but most people can expect to see significant improvement within 6 to 8 weeks. During this period, you may need to wear a splint and limit the use of your hand to allow for proper healing. Full recovery might take up to three months, but many people find that their symptoms are significantly reduced or eliminated after the surgery.
5. What are the best ways to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome?
Preventing carpal tunnel syndrome involves reducing strain on your wrists and maintaining good ergonomic habits. Key prevention tips include taking regular breaks from repetitive activities, using wrist splints if necessary, and performing stretching exercises to keep the wrist flexible. If your job involves typing or repetitive motions, ensure your workstation is set up to promote proper wrist alignment. Keeping your hands warm and avoiding excessive force during tasks can also help reduce your risk.

